Have you ever wondered how market research can significantly impact the success of a product? How can product managers effectively prioritize features and create a product backlog that truly delights customers? In the dynamic world of product management, understanding customer preferences and aligning them with product development is crucial. This is where Kano Analysis comes into play. Let’s delve into the world of market research and discover how Kano Analysis can answer pivotal questions that product managers often face.
What is Kano Analysis?
In the world of market research, one framework stands out as a game-changer in understanding customer preferences and driving product success: Kano Analysis. This powerful technique has revolutionized the way companies prioritize features and delight their customers.
A Brief History of Kano Analysis:
The roots of Kano Analysis can be traced back to the work of Dr. Noriaki Kano, a Japanese professor and quality management expert. In the early 1980s, Dr. Kano set out to explore the relationship between product features and customer satisfaction. His research aimed to uncover the underlying factors that differentiate successful products from the rest. Dr. Kano’s ground-breaking research quickly gained recognition, and his analysis framework was first applied in the manufacturing industry.
Japanese companies, renowned for their commitment to quality and continuous improvement, were among the early adopters of Kano Analysis. This technique provided them with a competitive edge by enabling them to prioritize features effectively and align their products with customer expectations.
Industry Veterans Supporting Kano Analysis:
Over the years, Kano Analysis has gained significant acclaim and endorsement from industry veterans across various sectors. Notable experts and organizations recognize the value and impact of this research technique:
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization): The ISO has recognized the significance of Kano Analysis and its application in quality management. It has incorporated Kano Analysis into its standards, further solidifying its credibility.
- Leading Companies: Prominent companies worldwide, spanning industries such as technology, automotive, and consumer goods, have embraced Kano Analysis to shape their product strategies. Examples include Toyota, Apple, and Samsung.
By leveraging Kano Analysis, these industry leaders have been able to gain deep insights into customer preferences, create innovative products, and establish strong market positions.
The Impact and Goals of Kano Analysis
Kano Analysis offers numerous benefits and helps organizations achieve specific goals by providing valuable insights into customer preferences. Let’s explore the impact of Kano Analysis and the goals it helps organizations accomplish:
Customer-Centric Product Development
- Understand customer needs: Kano Analysis enables organizations to gain deep insights into customer preferences, desires, and expectations.
- Design customer-centric products: By identifying what features are most valued by customers, organizations can tailor their product development efforts to meet customer needs effectively.
- Enhance user experience: Kano Analysis helps organizations create products that align with customer desires, resulting in improved user satisfaction and loyalty.
Effective Feature Prioritization
- Identify critical features: Kano Analysis assists in identifying and prioritizing features that are essential to customer satisfaction, ensuring their inclusion in the product roadmap.
- Optimize resource allocation: By understanding feature preferences, organizations can allocate resources effectively, focusing on developing the most impactful features that align with customer expectations.
- Streamline product backlogs: Kano Analysis enables product managers to organize and prioritize product backlogs based on customer needs, maximizing the value delivered by each feature.
Competitive Advantage
- Differentiate from competitors: Kano Analysis helps organizations identify unique and unexpected features that can set their products apart from competitors, providing a competitive edge in the market.
- Anticipate market trends: By continuously analyzing customer preferences, organizations can stay ahead of market trends, identifying emerging customer needs and incorporating them into their product strategies.
- Enhance brand reputation: Delivering products that consistently meet or exceed customer expectations helps build a strong brand reputation, leading to customer loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
Resource Optimization
- Efficient use of resources: Kano Analysis allows organizations to allocate resources strategically, focusing on developing features that have the greatest impact on customer satisfaction.
- Avoid unnecessary efforts: By understanding which features are indifferent to customers, organizations can avoid investing time and resources in developing low-value or non-essential features.
- Optimal pricing strategies: Kano Analysis aids organizations in setting prices based on the perceived value of different features, maximizing revenue potential.
Continuous Improvement
- Iterate and refine: Kano Analysis promotes a culture of continuous improvement by providing ongoing insights into changing customer preferences, allowing organizations to adapt their products accordingly.
- Stay relevant in the market: By continuously monitoring customer needs, organizations can ensure their products remain relevant and competitive in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
By leveraging Kano Analysis, organizations can align their product strategies with customer expectations, optimize resource allocation, differentiate themselves from competitors, and achieve greater customer satisfaction and loyalty. Embracing this powerful market research technique empowers organizations to deliver products that truly resonate with their target audience.
The 2 Dimensions of Kano Analysis: Understanding Customer Satisfaction and Functionality
Kano Analysis encompasses two essential dimensions: Customer Satisfaction and Functionality. Let’s explore each dimension in detail and understand their significance in evaluating product features.
Customer Satisfaction Dimension
The Customer Satisfaction dimension captures the emotional response of customers towards product features. It gauges how customers feel about the presence or absence of certain attributes. The scale for this dimension ranges from Delighted to Frustrated, indicating varying levels of customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
Examples of Customer Satisfaction Levels:
- Delighted: Features that exceed customer expectations and generate a sense of delight or surprise. Example: A smartphone that offers a built-in AI personal assistant.
- Satisfied: Features that meet or fulfill customer expectations. Example: A mobile banking app with a user-friendly interface and efficient transaction processing.
- Neutral: Features that customers neither appreciate nor dislike significantly. Example: A standard calculator function on a smartphone.
- Dissatisfied: Features that fall short of customer expectations and create dissatisfaction. Example: Frequent software crashes or system errors on a productivity application.
- Frustrated: Features that hinder or frustrate customers, leading to a negative user experience. Example: Slow response times or poor customer support.
Functionality Dimension:
The Functionality dimension assesses the level of feature implementation or functionality provided by a product. It helps determine how well a particular attribute is executed. The scale for this dimension ranges from None to Best, representing different levels of feature functionality.
Examples of Functionality Levels:
- None: Features that are completely absent or not implemented. Example: A camera-less smartphone lacking any photography capabilities.
- Some: Features that are partially implemented but lack comprehensive functionality. Example: A messaging app with basic text messaging but lacking multimedia sharing.
- Basic: Features that provide essential functionality but may lack advanced capabilities. Example: A word processing software that allows basic formatting and editing.
- Good: Features that are well-implemented and fulfill most user requirements. Example: A music streaming service with an extensive library and customizable playlists.
- Best: Features that offer superior performance and surpass user expectations. Example: A high-end graphics card that delivers exceptional gaming performance.
Understanding these dimensions helps product managers identify the level of satisfaction associated with various features and evaluate the functional capabilities of their products. By considering both dimensions, product managers can effectively prioritize features and optimize customer satisfaction.
Remember, the aim of Kano Analysis is to uncover the relationship between customer satisfaction, feature implementation, and the impact of different attributes on overall product perception. This understanding empowers product managers to make informed decisions and deliver products that align with customer expectations.
The Four Categories of Features in Kano Analysis: Decoding Customer Expectations
Kano Analysis utilizes two dimensions—Customer Satisfaction and Feature Implementation—to classify product features into four distinct categories: Must-Be, One-Dimensional, Attractive, and Indifferent. Each category represents different levels of customer expectations and provides crucial insights for product managers to effectively prioritize their feature development efforts.
Kano Analysis classifies product features into four distinct categories based on the two dimensions mentioned above Customer Satisfaction and Feature Implementation. Each category provides valuable insights into customer preferences, helping product managers prioritize feature development effectively. Let’s delve into each category and explore how they are calculated, what they represent, and provide detailed examples for a better understanding.
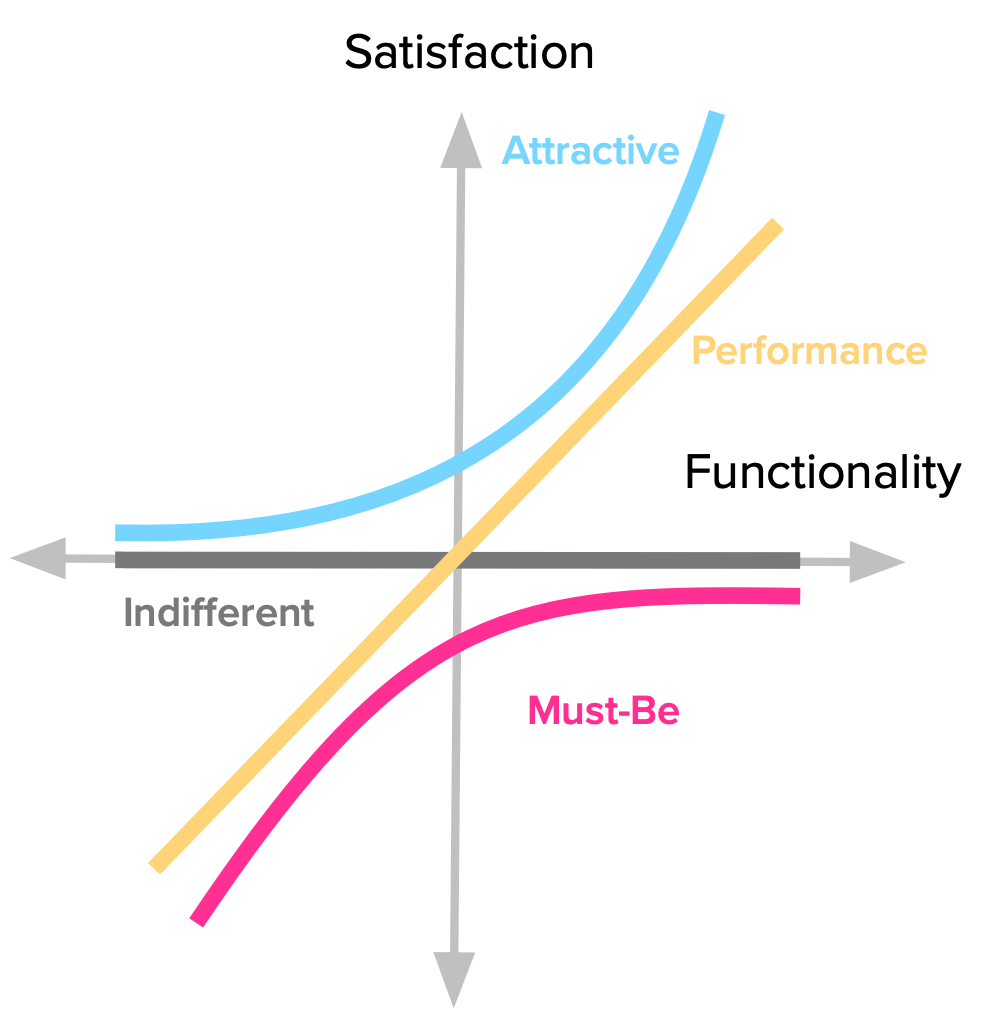
Click here for image source for all the 4 catgories
Must-Be Features (Threshold Attributes):
- Calculation: Must-Be features are determined by a negative correlation between customer satisfaction and feature implementation. If a Must-Be feature is missing or poorly implemented, customers will be highly dissatisfied. However, the satisfaction level does not increase linearly as the feature is adequately implemented; it simply meets the basic expectations.
- Representation and Meaning: Must-Be features represent the minimum requirements for customers to consider a product viable. They are essential for achieving customer satisfaction and avoiding dissatisfaction. These features are typically expected by customers and are taken for granted when present. Failure to meet Must-Be requirements can result in customer attrition and negative reviews.
- Example: Consider a smartphone without a functioning touch screen. The absence of this feature would lead to significant dissatisfaction among customers. However, as long as the touch screen works as expected, additional improvements or advanced functionalities would not significantly impact satisfaction. In this case, the touch screen is a Must-Be feature that customers expect as a basic requirement.
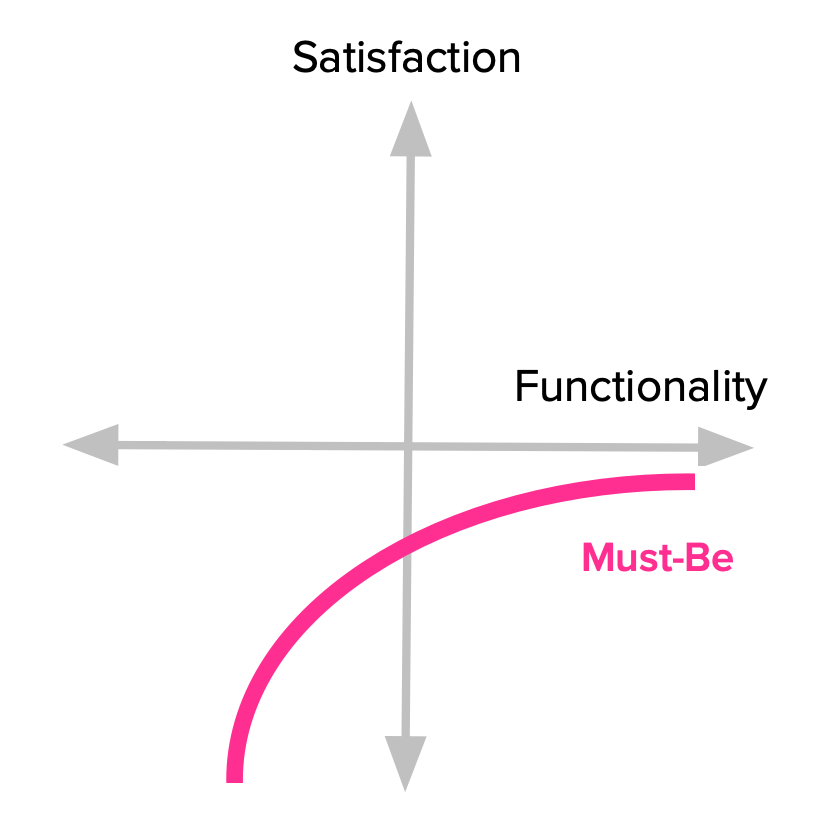
One-Dimensional Features (Performance Attributes)
- Calculation: One-Dimensional features are positively correlated with customer satisfaction and exhibit a linear relationship with feature implementation. As the implementation of these features improves, customer satisfaction increases proportionally.
- Representation and Meaning: One-Dimensional features have a direct impact on customer satisfaction, and customers’ expectations increase as the features are enhanced. These features provide opportunities for differentiation among competitors and play a crucial role in meeting customers’ evolving needs and preferences.
- Example: Consider a music streaming service that offers personalized playlists based on users’ listening history. The more accurately the service curates and recommends songs based on user preferences, the more satisfied customers become. Enhancements in the recommendation algorithm, user interface, or playlist customization options would directly contribute to increased customer satisfaction.
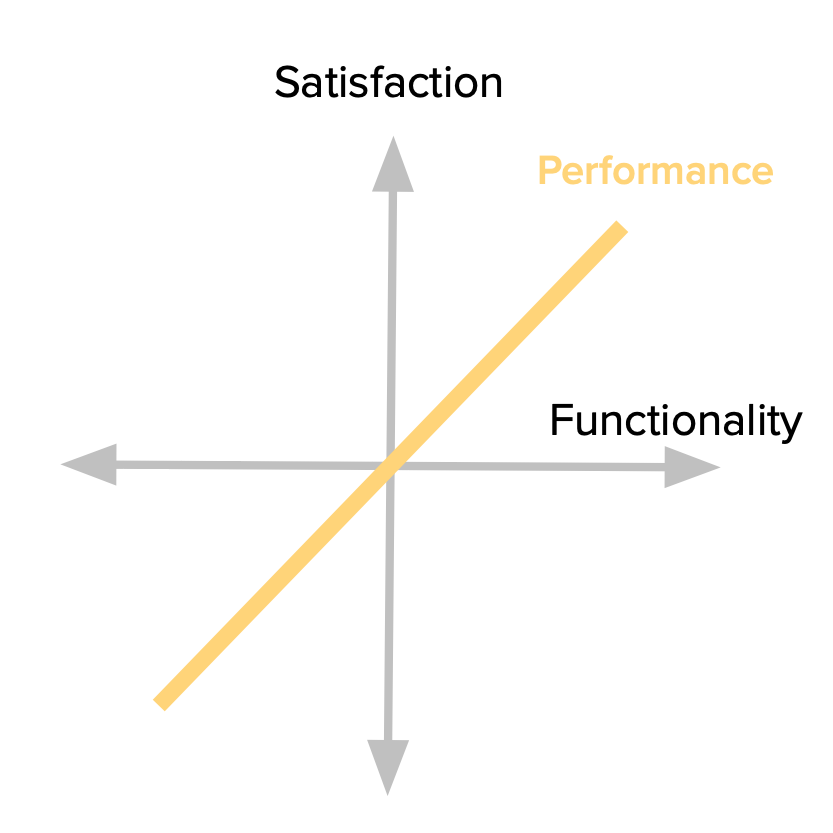
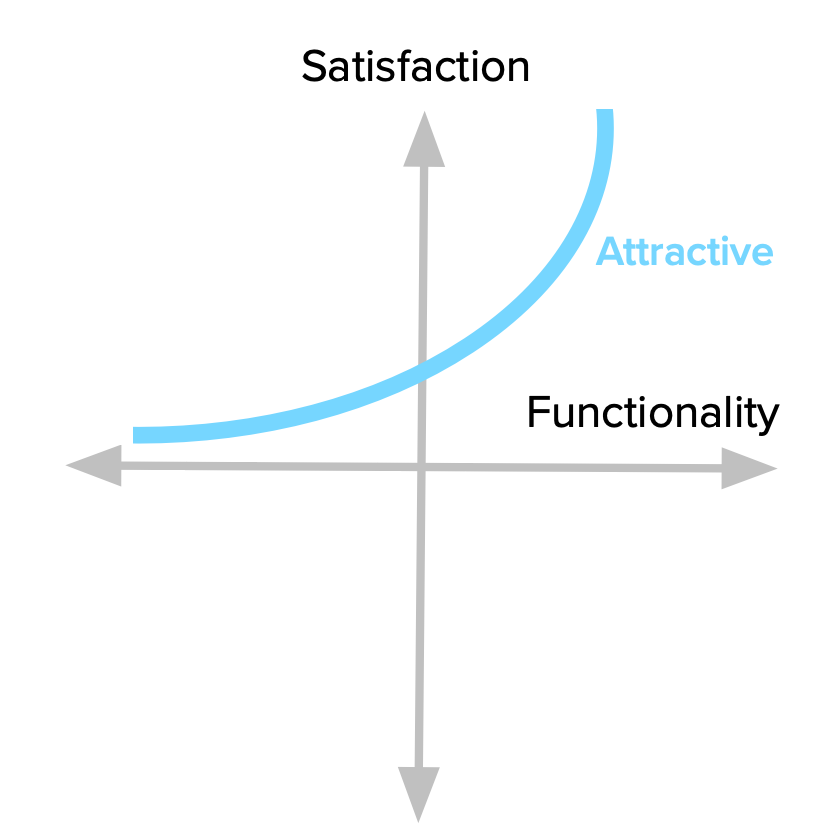
Attractive Features (Excitement/Delight Attributes)
- Calculation: Attractive features have a unique characteristic—they do not have a linear correlation with customer satisfaction. Instead, they create a disproportionate impact on satisfaction when implemented. These features are unexpected and often go beyond customers’ initial expectations, generating excitement and positive emotions.
- Representation and Meaning: Attractive features differentiate a product from its competitors and provide a “wow” factor that delights customers. They have the potential to evoke positive emotions, build brand loyalty, and contribute to customer retention. Product managers need to carefully identify and prioritize these features to captivate customers and create a memorable experience.
- Example: Imagine a camera app that introduces a feature allowing users to apply real-time augmented reality filters to their photos. This unexpected and innovative feature would pleasantly surprise customers, adding an element of excitement and creativity to their photography experience. Attractive features like this enhance the product’s desirability and generate positive word-of-mouth referrals.
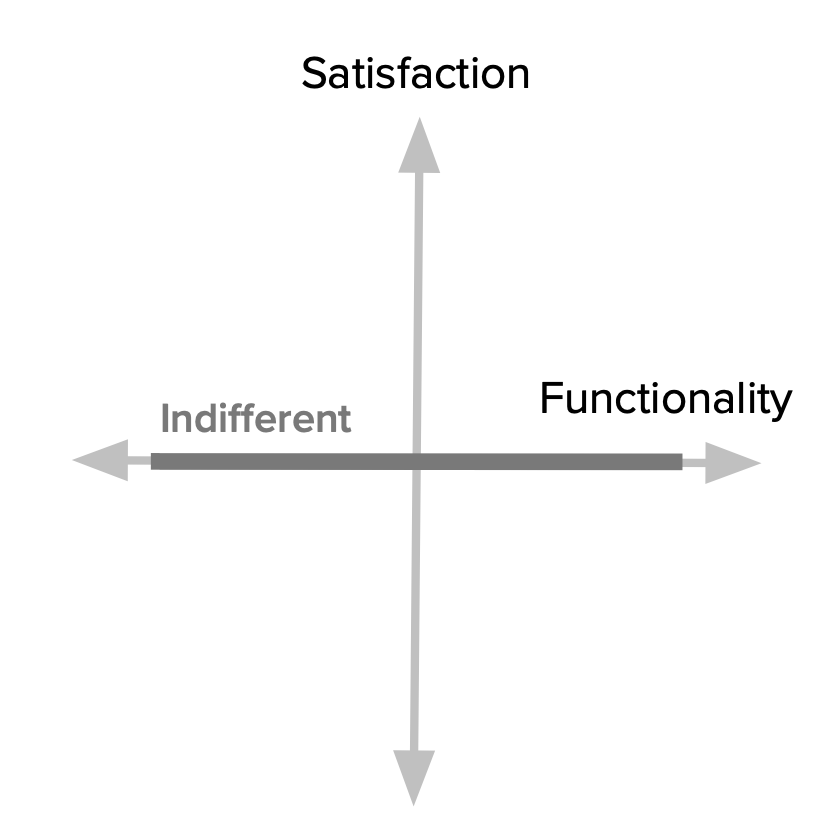
Indifferent Features
- Calculation: Indifferent features do not exhibit a significant correlation with customer satisfaction. The presence or absence of these features has little to no impact on customer perception or satisfaction levels. Customers remain relatively neutral regardless of the implementation or exclusion of these features.
- Representation and Meaning: Indifferent features are neither expected nor desired by customers, as they have minimal influence on satisfaction. Allocating resources to develop or improve indifferent features may not yield substantial benefits in terms of customer satisfaction or competitive advantage. Product managers should exercise caution and focus on features that deliver higher customer value instead.
- Example: In a food delivery app, the option to change the background colour of the user interface would likely be considered an indifferent feature. Customers may not have a preference for or against this feature, and its presence or absence would not significantly impact their satisfaction or usage of the app.
Understanding the four categories of Kano Analysis provides product managers with a comprehensive understanding of customer preferences. By strategically prioritizing Must-Be features, optimizing One-Dimensional features, incorporating Attractive features, and avoiding unnecessary investments in Indifferent features, product managers can align their development efforts with customer demands, enhance customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Steps to Use Kano Analysis Effectively
1 – Define Product Features
- Introduction: The first step in conducting Kano Analysis is to define the features of your product. This involves identifying and listing all the potential features that your product offers.
- Objective: The objective of this step is to create a comprehensive list of product features that will be analyzed using the Kano framework.
- Acceptance Criteria: A well-defined list of product features should be compiled, ensuring that each feature is clear and unambiguous.
- Best Practices:
- Collaborate with stakeholders: Engage with cross-functional teams, including product managers, designers, engineers, and marketing personnel, to gather a comprehensive understanding of the product’s features.
- Conduct market research: Analyze industry trends, customer feedback, and competitor offerings to identify potential features that align with customer expectations.
- Prioritize simplicity: Keep the feature list manageable and focused on the core value proposition of the product.
- Consider scalability: Anticipate future iterations of the product and ensure that the feature list accommodates potential expansions.
- Things to Consider:
- Avoid feature overlap: Ensure that each feature is distinct and does not overlap with others in terms of functionality.
- Eliminate ambiguous features: Refine the feature list to remove any vague or poorly defined features that could lead to confusion during analysis.
- Example: Let’s consider a mobile application for a food delivery service. The defined features may include order placement, real-time tracking, payment options, customer reviews, and personalized recommendations.
2 – Conduct Customer Surveys
- Introduction: Once the product features are defined, the next step is to collect customer feedback through surveys. These surveys aim to capture customer preferences, satisfaction levels, and expectations related to the identified features.
- Objective: The objective of this step is to gather data that will be used to classify the features into the appropriate Kano categories.
- Acceptance Criteria: A sufficient number of survey responses should be collected, ensuring a diverse representation of the target customer segment.
- Best Practices:
- Use a structured questionnaire: Design a survey with clear and specific questions that capture customer preferences and satisfaction levels for each feature.
- Ensure survey anonymity: Assure respondents that their identities will remain confidential, encouraging honest and unbiased feedback.
- Consider sample size: Aim for a statistically significant sample size to ensure reliable data analysis.
- Target the right audience: Ensure the survey is distributed to the target customer segment that accurately represents the product’s user base.
- Things to Consider:
- Avoid leading questions: Frame questions objectively to avoid biasing respondents’ answers.
- Incorporate open-ended questions: Supplement closed-ended questions with open-ended ones to gather qualitative insights and valuable feedback.
- Example: In our food delivery app scenario, the customer survey may include questions about the importance of real-time order tracking, preferred payment methods, satisfaction with delivery times, and feedback on personalized recommendations.
3 – Analyze Survey Results
- Introduction: After collecting survey responses, the next step is to analyze the data to classify the features into the appropriate Kano categories. This analysis will help determine the impact of each feature on customer satisfaction.
- Objective: The objective of this step is to identify which features fall into the Must-Be, One-Dimensional, Attractive, or Indifferent categories based on customer responses.
- Acceptance Criteria: The features should be accurately classified into the respective Kano categories, ensuring consistency and reliability in the analysis.
- Best Practices:
- Quantitative data analysis: Use statistical techniques to interpret survey responses, such as calculating mean satisfaction ratings for each feature.
- Visualize data: Create charts or graphs to present the results visually, facilitating a clear understanding of feature categorization.
- Consider segmentation: Analyze survey results based on customer segments or demographics to identify any variations in preferences.
- Validate findings: Seek feedback from stakeholders and subject matter experts to validate the categorization of features.
- Things to Consider:
- Handle outliers: Account for extreme responses that may skew the analysis by identifying and addressing outliers.
- Examine correlations: Look for relationships between features to uncover potential dependencies or interactions.
- Example: In the food delivery app analysis, survey responses indicating high customer satisfaction with real-time order tracking may classify this feature as a One-Dimensional feature.
4 – Prioritize Feature Development
- Introduction: Once the features are categorized, the next step is to prioritize their development based on the Kano analysis results. This step involves determining which features to focus on and in what order.
- Objective: The objective of this step is to establish a clear roadmap for feature development, ensuring resources are allocated effectively.
- Acceptance Criteria: Create a list of prioritized features, taking into account the categorization and impact on customer satisfaction.
- Best Practices:
- Focus on Must-Be features: Allocate resources to address Must-Be features first to meet customers’ basic expectations.
- Enhance One-Dimensional features: Prioritize the development of One-Dimensional features to increase customer satisfaction linearly.
- Differentiate with Attractive features: Invest in developing Attractive features that differentiate your product from competitors and create delight.
- Consider technical feasibility: Evaluate the technical feasibility and resources required for each feature before prioritizing them.
- Things to Consider:
- Balance long-term and short-term goals: Align feature development with both immediate customer needs and long-term product vision.
- Revisit prioritization regularly: Regularly reassess customer preferences and market dynamics to update the feature prioritization as needed.
- Example: Based on the Kano analysis, the food delivery app team may prioritize enhancing the real-time order tracking feature (One-Dimensional) to further improve customer satisfaction and differentiate their app from competitors.
By following these steps and leveraging the insights from Kano Analysis, product managers can make informed decisions, prioritize feature development, and deliver products that align with customer expectations.
Final Thoughts for Product Managers
Product managers play a crucial role in driving product success by understanding customer needs, prioritizing features, and delivering exceptional user experiences. As we conclude this comprehensive guide to Kano Analysis, let’s delve into some key takeaways and best practices for product managers to effectively leverage this framework and excel in their roles.
Embrace a Customer-Centric Mindset
Successful product managers understand that customer satisfaction is paramount. They recognize the importance of gathering customer feedback, conducting market research, and using frameworks like Kano Analysis to align product features with customer preferences. By adopting a customer-centric mindset, product managers can ensure that their decisions are guided by the needs and desires of the target audience. In the space of outcomes for product managers, customer satisfaction will always take precedence.
Continuously Listen to Customer Feedback
The voice of the customer should be an ongoing source of inspiration and guidance for product managers. Regularly collect customer feedback through surveys, interviews, and user testing sessions. This valuable input provides insights into emerging trends, evolving customer expectations, and areas for improvement. By actively listening to customers, product managers can stay ahead of the competition and deliver products that meet or exceed expectations.
Prioritize Must-Be and One-Dimensional Features
Kano Analysis helps product managers understand the criticality of different feature categories. Must-Be features represent the baseline expectations of customers, while One-Dimensional features have a linear relationship with satisfaction. Product managers should prioritize the development and enhancement of these categories to ensure that the product meets the fundamental needs of customers and performs optimally.
Innovate with Excitement Features
While meeting basic customer expectations is vital, product managers must also focus on creating differentiation and delight. Excitement features, the Attractive category in Kano Analysis, have the potential to surprise and captivate customers. These features go beyond expectations and create a memorable user experience. Product managers should encourage innovation and explore opportunities to incorporate exciting and unique features that set their products apart from competitors.
Iterate and Refine
Product development is an iterative process. Successful product managers continuously evaluate and refine their product roadmaps based on market dynamics, customer feedback, and evolving business goals. Kano Analysis provides a framework for understanding changing customer preferences and aligning feature development accordingly. Product managers should regularly reassess customer needs, prioritize feature enhancements, and adapt their strategies to meet market demands.
Collaborate and Communicate Effectively
Product managers serve as the bridge between various stakeholders, including customers, development teams, and executive leadership. Everyone must align with the product vision and goals through effective collaboration and communication. Product managers should facilitate open and transparent communication, actively engage with cross-functional teams, and create a shared understanding of the product roadmap and feature priorities. This collaboration fosters a culture of innovation, accountability, and shared ownership of product success.
Continual Learning and Improvement
The field of product management is dynamic and ever-evolving. To stay ahead, product managers must be lifelong learners. Seek opportunities to enhance your knowledge of market research methodologies, statistical analysis, and customer behavior. Stay updated on industry trends, attend conferences, join professional networks, and invest in personal development. By continuously improving your skills and staying abreast of industry advancements, you can navigate the complexities of product management with confidence.
In conclusion, Kano Analysis serves as a powerful tool for product managers to understand customer preferences, prioritize features effectively, and drive customer satisfaction. By incorporating this framework into their market research practices, product managers can make data-driven decisions, develop customer-centric products, and stay ahead of the competition. Remember to embrace a customer-centric mindset, listen to customer feedback, prioritize features strategically, and foster effective collaboration. Continual learning and improvement are key to success in the ever-changing landscape of product management. Armed with these insights and a solid understanding of Kano Analysis, product managers can unlock the full potential of their products and deliver exceptional value to their customers.